U-boot代码框架介绍
目录
1. 介绍
本文主要介绍了Uboot 的代码框架。其中主要包含了矽昌自主添加的功能和uboot中的命令操作使用描述。
1.1. 适用人员
需要使用uboot的人员。
1.2. 开发环境
- 可以正常编译通过的Siflower SDK环境
该环境的搭建请参考快速入门
1.3 功能概述
本文介绍了U-boot的结构和uboot命令行操作使用方法。
2. Uboot代码框架描述
2.1 U-boot的介绍
bare spl
SPL是介于芯片内部rom程序与uboot之间的一个BootLoader,其主要功能为初始化ddr,系统管理器,时钟,以及加载uboot。SPL程序本身需要加载到系统内部ram中运行,是一个轻量级的uboot。
在U-boot开源程序中,本身是包含SPL选项的。FULLMASK版本将芯片内部ram减少到了64KB,不足以同时支持Uboot-spl的rom+ram的需求,因此采用了一份裸机实现的bare_spl。
Bare_spl相比于原Uboot-spl更加简单可控,也可以同样实现引导uboot的功能。同时,bare_spl也同时支持mpw0和mpw1芯片,并且减少了存储空间,为flash优化、分区的重新定义提供了支持。
SPL的流程如下(uboot-spl和bare-spl实现主要功能一致):
graph TB
title(SPL 流程图)
A(IROM) --> B[CPU初始化]
B --> C[板级初始化]
C --> D[DDR初始化]
D --> E[从device读取镜像]
E --> F[校验镜像信息]
F --> G[跳转到uboot]
G --> H[uboot]
在bare_spl中,默认支持三种boot device:spi-flash,sd card,emmc。按照spi>sd>emmc的优先级,只要检测到device存在,spl便会自动从其启动。因此如果想要在同时包含spi-flash与sd的板子中,使用sd作为device存放uboot镜像,需要定义SKIP_SPI_FLASH。由于spi与emmc存在复用关系,因此不会同时存在。Uboot-spl需要在编译阶段就指定使用哪一种boot device。而SF19A2890目前仅支持一种boot device:spi-flash,依据读取flash型号决定使用nand falsh还是nor flash。
SPL与uboot相同,引导的镜像需要包含一个uimage的header,其中会包含所引导镜像的类型。因此,SPL不只可以引导uboot,进而启动内核,还可以引导pcba测试程序。
U-boot
Uboot的启动分为两个阶段:stage1和stage2。stage1可以认为是uboot认定的rom阶段,stage2是ram阶段。Stage1向stage2转换的主要标志就是代码段的relocation,即将代码段从“rom”复制到“ram”。
Uboot的流程图如下:
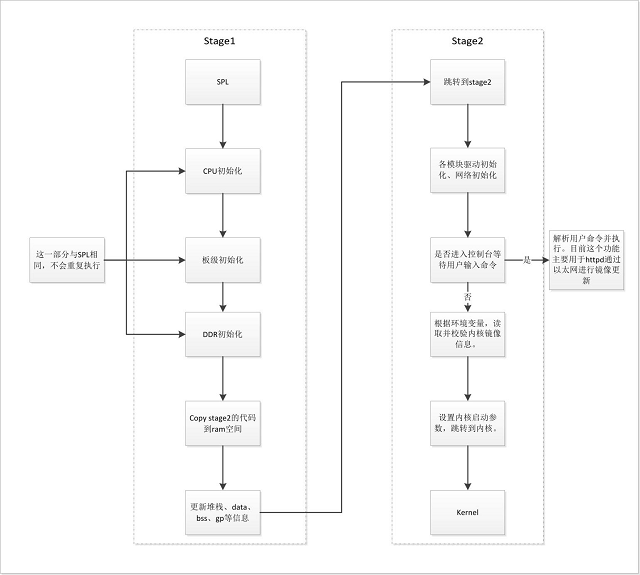
每个stage都有一个主要执行的函数序列,即init_sequence_f和init_sequence_r。由于SPL的存在,uboot的stage1其实并没有什么实质性的功能,整个uboot都是运行在ddr上的。在进入stage2前,uboot会进行一个代码段的重定向,由于uboot本身是位置无关的,因此只需要同时更新堆栈信息,全局变量表等即可,重定向后的代码依旧可以正常执行。按照uboot的思想,这个stage2是运行在ram中的,因此速度要比stage1要快。
init_sequence_r中主要是进行了各个模块驱动的初始化,网络的初始化和一些其他准备工作,比如环境变量的初始化等。在准备结束后,uboot最终会进入一个main_loop,进行控制台的初始化。此时uboot提供了一个3s的倒计时,如果不在时间内从控制台(默认串口)进行输入,则会进入自动启动流程,根据预设的环境变量参数,进行引导启动;如果有输入,就可以停下来进入控制台,与uboot进行交互。此时uboot会根据输入的命令情况进行解析并执行。命令具体的使用和介绍见后文。
2.2 uboot源码整体框架
下面简要整理了uboot源码中主要文件和文件夹的大致功能描述:
| 文件路径 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| bare_spl | 初始化ddr,系统管理器,时钟,以及加载uboot镜像文件 |
| arch/mips/cpu | 与处理器相关的文件。每个子目录中都包括cpu.c和interrupt.c、start.S、u-boot.lds。 |
| cpu.c:初始化CPU、设置指令Cache和数据Cache等 | |
| interrupt.c:设置系统的各种中断和异常 | |
| start.S:是U-boot启动时执行的第一个文件,它主要做最早期的系统初始化,代码重定向和设置系统堆栈,为进入U-boot第二阶段的C程序奠定基础。 | |
| u-boot.lds:链接脚本文件,对于代码的最后组装非常重要。 | |
| board/siflower/ | 对应开发板相关文件 |
| common | 与处理器体系结构无关的通用代码,U-boot的命令解析代码/common/command.c、所有命令的上层代码cmd.c、U-boot环境变量处理代码env.c等都位于该目录下 |
| drivers | 包含几乎所有外围芯片的驱动,网卡、USB、串口、LCD、Nand Flash等等 |
| disk fs net | 支持CPU无关的重要子系统: |
| 磁盘驱动的分区处理代码 | |
| 文件系统:FAT、JFFS2、EXT2等 | |
| 网络协议:NFS、TFTP、RARP、DHCP等等 | |
| include | 头文件,包括各CPU的寄存器定义,文件系统、网络等等 |
| configs子目录下的文件是与目标板相关的配置头文件 | |
| doc | U-Boot的说明文档,在修改配置文件的时候可能用得上 |
| Makefile MAKEALL config.mk | 控制整个编译过程的主Makefile文件和规则文件 |
| tools | 编译S-Record或U-Boot映像等相关工具,制作bootm引导的内核映像文件工具mkimage源码 |
| MAINTAINERS README | 介绍性的文档、版权说明 |
| httpd | 以太网驱动,httpd服务,主要用于在uboot中进行镜像文件更新 |
2.3 Siflower uboot个性化设计
uboot以太网网页烧录镜像更新功能
主要功能是用于在uboot命令行中,使用http协议进行开发板镜像文件更新(包含了uboot和kernel镜像文件的两种更新方式),详见《# U-boot移植应用开发手册》以太网烧录章节描述。
bare_spl 框架设计
为了节约内存空间独立设计的裸机代码,主要功能为初始化ddr,系统管理器,时钟,以及加载uboot。在fullmask中,启动设备支持使用norflash和nandflash两种类型。
模块节能设置
为了降低各模块和总线在放开的情况下的功耗,在uboot将所有可操作模块和总线复位等信号都控制住,可以从根本上降低了系统起来之后的能耗。在kernel boot起来之后,可以根据实际需求打开各自模块和总线的复位使能和时钟开关。
3 uboot操作指令
3.1 添加uboot命令
1.在uboot下建立 cmd/命令.c 文件;
2.用 U_BOOT_CMD 来定义命令;
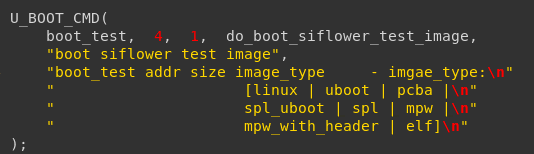
对应参数分别为:name:命令名;maxargs:命令的最大参数个数;repeatable:是否自动重复(按Enter键是否会重复执行);command:该命令对应的响应函数指针;usage:简短的使用说明;help:较详细的使用说明。
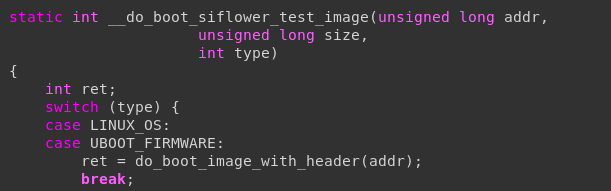
3.在 cmd/命令.c 文件中实现命令的操作do命令函数
4.将 cmd/命令.c 添加到 cmd/Makefile 中;
5.重新编译并烧录uboot镜像。
3.2 uboot下现有命令及描述
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ? | alias for ‘help’ |
| base | print or set address offset (base 显示偏移量;base + offset 重新设置偏移量) |
| bdinfo | print Board Info structure |
| boot | boot default, i.e., run ‘bootcmd’ |
| boot_test | boot siflower test image |
| bootd | boot default, i.e., run ‘bootcmd’ |
| bootelf | Boot from an ELF image in memory |
| bootm | boot application image from memory |
| #bootp | boot image via network using BOOTP/TFTP protocol |
| bootvx | Boot vxWorks from an ELF image |
| btn_httpd_detect | check pmu buttom to run httpd(在无法使用串口的情况下,通过按键,通知到CPU,然后用代码去将httpd更新指令输入到串口中,就可以在网页上进行镜像文件更新) |
| cmp | compare memory (cmp [.b, .w, .l] addr1 addr2 count,.b以字节为单位,.w以字为单位,.l以长字为单位。注意:cmp.b中间不能保留空格,需要连续敲入命令。第1个参数addr1是第一块内存的起始地址,第2个参数addr2是第二块内存的起始地址,第3个参数count是要比较的数目,单位按照字节、字或者长字。) |
| coninfo | print console devices and information |
| cp | copy memory (cp [.b, .w, .l] source target count,第1个参数source是要复制的数据块起始地址,第2个参数target是数据块要复制到的地址。这个地址如果在Flash中,那么会直接调用写Flash的函数操作。所以U-Boot写Flash就使用这个命令,当然需要先把对应Flash区域擦干净,第3个参数count是要复制的数目,根据cp.b cp.w cp.l分别以字节、字、长字为单位。) |
| crc32 | checksum calculation(crc32 address count [addr],第1个参数address是需要校验的数据起始地址,第2个参数count是要校验的数据字节数,第3个参数addr用来指定保存结果的地址。) |
| dm | Drive model low level access(dm tree ,Dump drive model tree;dm uclass,Dump list of instances fo each uclass;dm devres,Dump list of device resources for each device) |
| echo | echo args to console(echo [args]) |
| editenv | edit environment variable(editenv name,edit environment viriable ‘name’ ) |
| #env | environment handling commands(default [-f] -a - [forcibly] ,reset default environment;env default [-f] var […] - [forcibly] ,reset variable(s) to their default values;env delete [-f] var […] - [forcibly] ,delete variable;env edit name ,edit environment variable;env exists name , tests for existence of variable;env flags,print variables that have non-default flags) |
| exit | exit script |
| false | do nothing,unsuccessfully |
| fdt | flattened device tree utility commands(fdt move |
| go | start application at address ‘addr’(go addr [arg …],start application at address ‘addr’) |
| help | print online help |
| httpd | start ww server for firmware recovery with [localAddress] |
| iminfo | print header information for application image |
| imxtract | extract a part of a multi-image |
| itest | return true/false on integer compare |
| loop | infinite loop on address range |
| lzmadec | lzma uncompress a memory region(lzmadec srcaddr dstaddr [dstsize]) |
| md | memory display(md[.b,.w,.l] address [# of objects]) |
| mm | memory modify (mm[.b,.w,.l] address) |
| mw | memory write (mw[.b,.w,.l] address value [count]) |
| nm | memory modify (nm[.b,.w,.l] address) |
| ping | send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network host |
| printenv | print environment variables |
| reset | Perform RESET of the CPU |
| rhreset | Rehold all module resets to save power |
| run | run commands in an environment variable (run var […],run the commands in an environment variables) |
| saveenv | save environment variables to persistent storage |
| setenv | set environment variables |
| sf | SPI flash sub-system(probe [[bus:]cs] [hz] [mode],init flash device on given SPI bus and chip select;sf read addr offset/partition len,read len' bytes starting at、offset’ or from start of mtd、partition'to memory at addr’;sf write addr offset/partition len,write len' bytes from memory、at addr’ to flash at offset'、or to start of mtd partition’;sf erase offset/partition [+]len,erase len' bytes from offset’、or from start of mtd partition'、+len’ round up len' to block size;sf update addr offset|partition len,erase and write len’ bytes from memory、at addr' to flash at offset’、or to start of mtd `partition’;sf protect lock/unlock sector len,protect/unprotect ‘len’ bytes starting、at address ‘sector’) |
| showvar | print local hushshell variables |
| spld | update spl from device |
| test | minimal test like /bin/sh |
| tftpboot | boot image via network using TFTP protocol |
| true | do nothing,successfully |
| version | print monitor,compiler and linker version |
文档信息
- 本文作者:Phoenix
- 本文链接:https://siflower.github.io/2022/03/23/ubootCodeFramework/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)